1. Noun: A word for a person, place, thing, or idea. Like "T-shirt", "cat", "park", "ball", or "happiness".
3. Before a noun ("lidwoord"): A word like: the or a/an: like the tree and a tree.
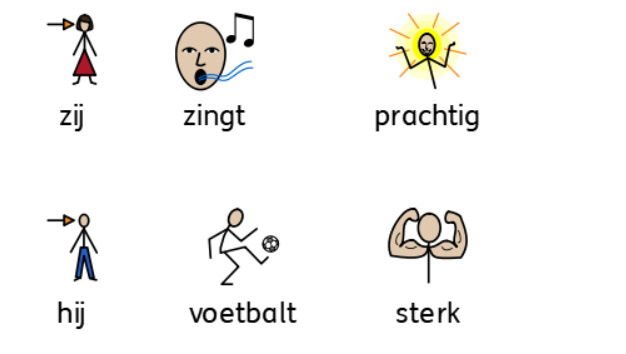
2. Verb: A word that indicates an action or a certain state. It tells what the noun is doing. Like "I love", "I run", "I am" or "I have".
3. Adjective: A word that describes a characteristic of a noun. It tells us more about a noun, like what it looks like, how it feels, or how many. Examples are "a big cat", "a blue sky".
4. Adverb: A word that often indicates: how, when, where, or how much. Examples include "quickly", "very", "tomorrow", or "almost".
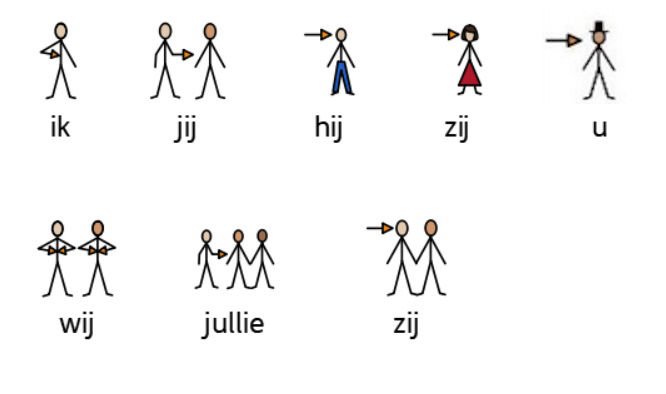
5. Personal Pronoun: Words like; I, you, he, she, we and they.
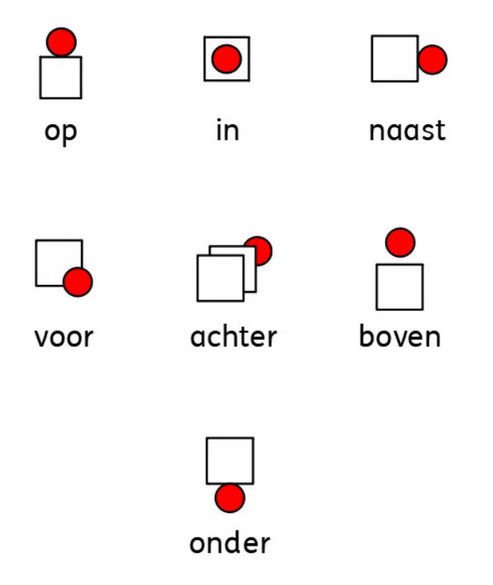
6. Preposition: A word that shows the relationship between a noun (or pronoun) and other words in a sentence. It often tells us where something is or when something happens. Examples are; "the dog is in the garden", "the girl sits on a chair".
7. Conjunction: A word that joins words, phrases, or sentences together. Like: it was a man and he was old
8. Sentence: A group of words that express a complete thought. It starts with a capital letter and ends with a period (.), question mark (?), or exclamation mark (!).
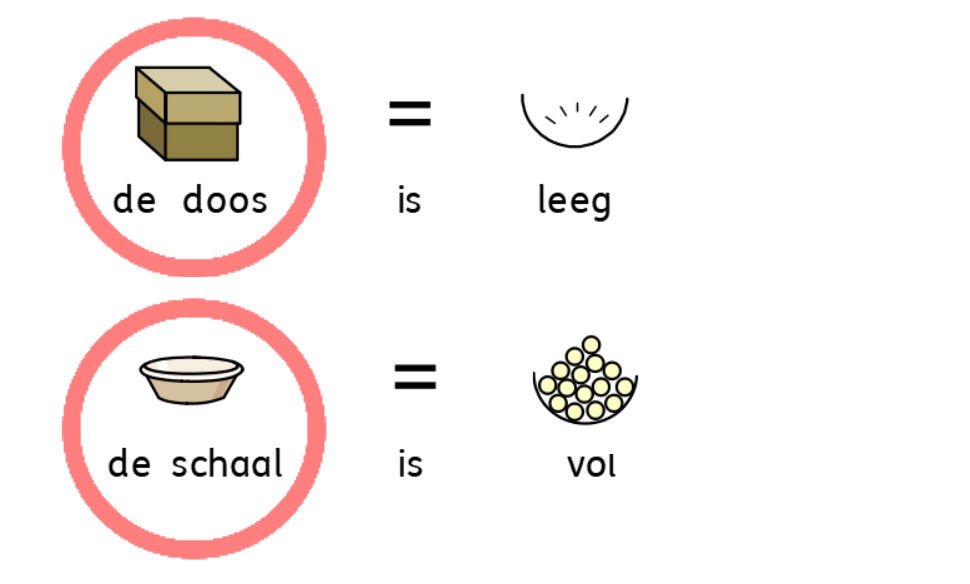
9. Subject: The part of the sentence that tells who or what the sentence is about. Usually, it's a noun or pronoun. Example: The box was empty.
10. The object "lijdend voorwerp") : The so called "direct object" in a sentence is a noun or pronoun that receives the action of the verb. It answers the question "what?" or "whom?" in relation to this verb. For instance if you say "I love Amsterdam" Amsterdam is the direct object as it is the answer to the question "what do you love?".
<<<